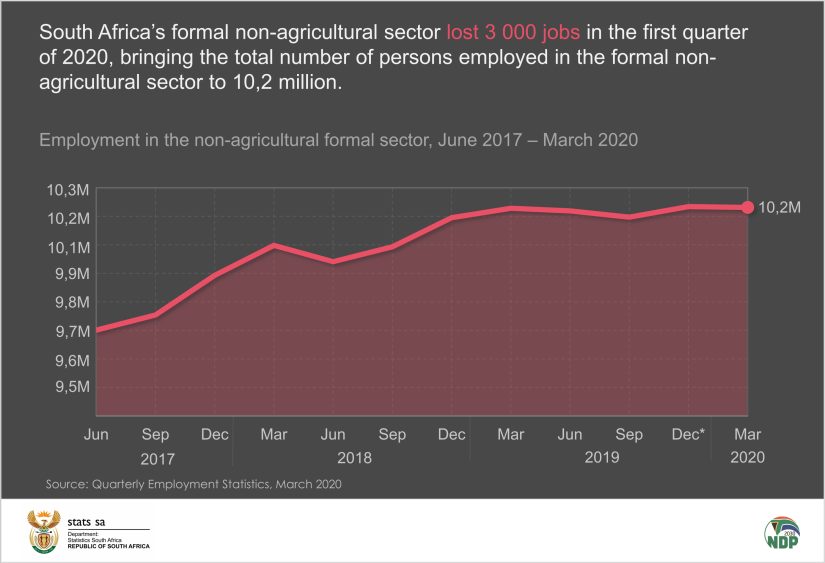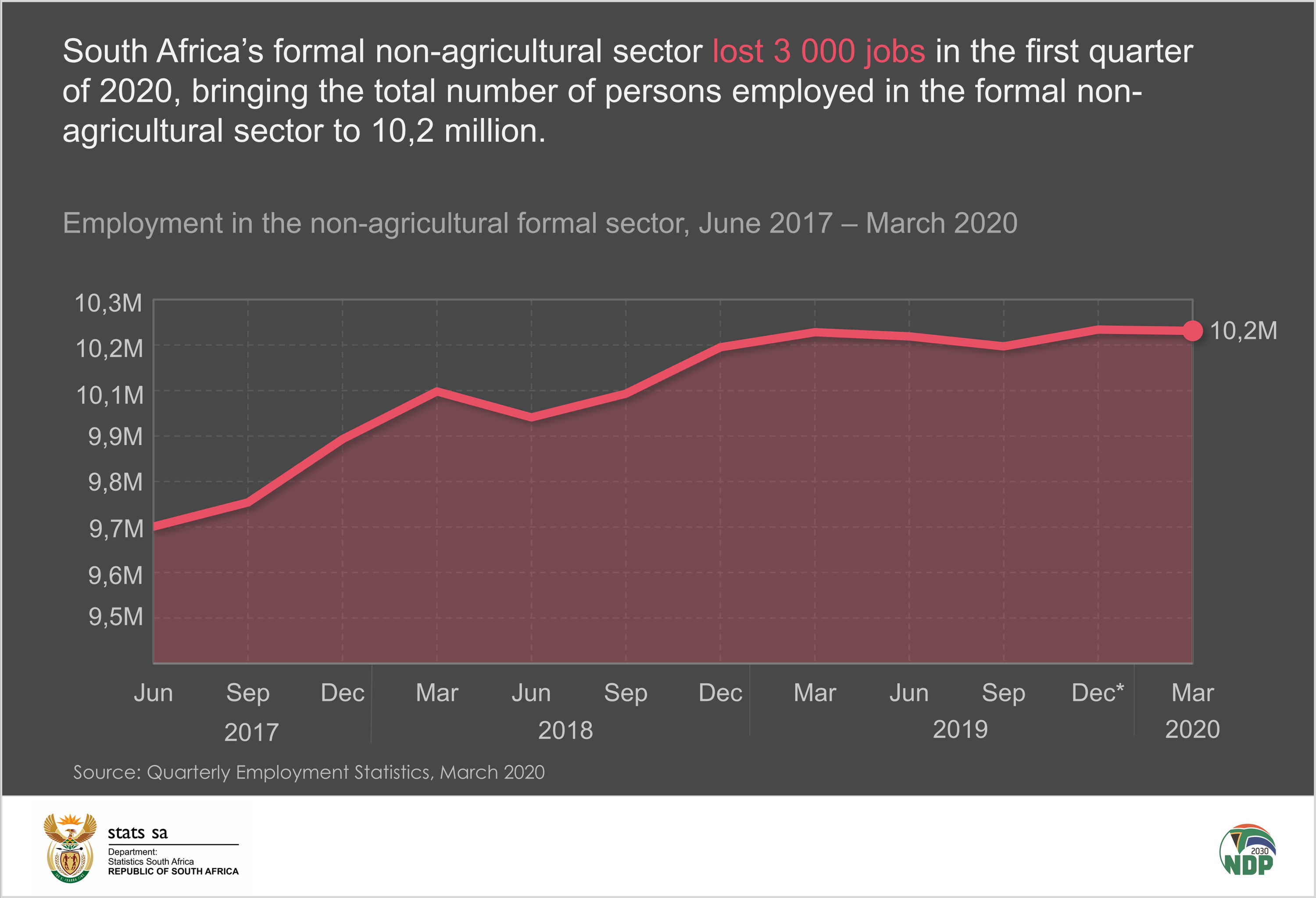
**Title: A Reevaluation of Employment Estimates: The Consequences of Incorrect 258,000 Job Data**
In the intricate realm of economic analysis, the precision of job estimates is pivotal in influencing policy decisions and financial markets. A recent mistake in job reporting, which erroneously indicated an increase of 258,000 jobs, highlights the significance of accuracy in economic statistics and its consequences across multiple sectors.
**Examining the Mistake**
The error consisted of an exaggeration of employment numbers, resulting in a fleeting alteration in the perception of economic health. Initial job growth statistics are frequently examined as indicators of economic well-being, offering insights into consumer expenditures, business expansion, and overall economic dynamism.
**The Immediate Response**
Upon publication, the incorrect data spurred a positive reaction in market sentiments. Investors commonly respond to such indicators with increased optimism, often propelling stock prices and affecting bond yields. These immediate reactions emphasize the markets’ responsive characteristic to employment statistics, considered as direct manifestations of economic circumstances.
**Economic and Policy Consequences**
Having faulty data can lead policymakers to make assumptions that may not reflect reality on the ground. For example, an exaggeration could hinder essential interventions or postpone policy changes aimed at boosting employment. Conversely, it might induce premature tightening of monetary policies based on the mistaken belief of an overheating economy.
**Effects Beyond Financial Markets**
The implications also reach businesses that depend on labor data for strategic planning. Inaccuracies can skew perspectives on wage pressures, talent acquisition methods, and operational scaling. Firms might adjust their hiring rates, salary structures, or investment in workforce development based on misinterpreted economic scenarios. Furthermore, individuals may base their career choices on distorted views of job availability and industry growth.
**Revisions and Modifications**
Once the error was identified, revisions were carried out to align with actual job figures, shifting public views and policy conversations. Although revisions are standard practice, their promptness and transparency are crucial for sustaining trust among stakeholders who depend on these figures for informed decision-making.
**Regaining Trust**
Initiatives to enhance data accuracy involve investments in robust methodologies, utilizing advanced technologies, and ensuring swift error correction processes. Organizations tasked with gathering and distributing economic data consistently refine their strategies to avert similar mistakes in the future, striving to restore confidence in their results.
**Conclusion**
The episode of the inaccurate 258,000 job figures acts as a strong reminder of the necessity for precision in economic reporting. As we navigate complex economic environments, the accuracy of available data remains crucial. Ensuring the dependability of job estimates is not merely an academic pursuit but a fundamental component of effective economic stewardship and decision-making.